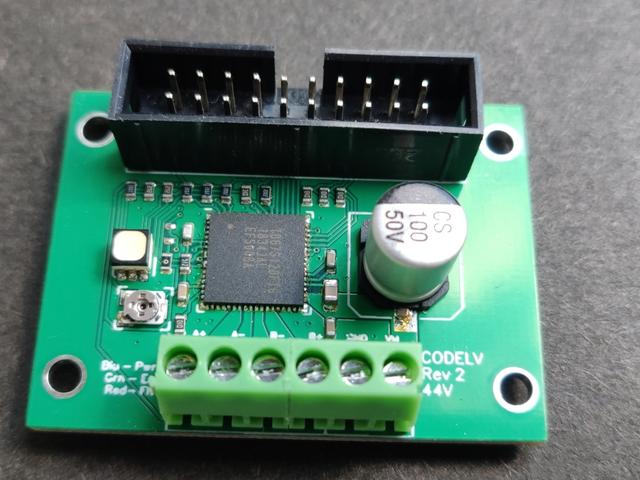

This is a single axis stepper motor breakout board using Toshiba's TB67S128FTG driver.
With proper cooling it can achieve about 2.2A continuous per-phase making it suitable to control most NEMA 17 and NEMA 23 stepper motors in parallel and some smaller NEMA 34 motors in series.
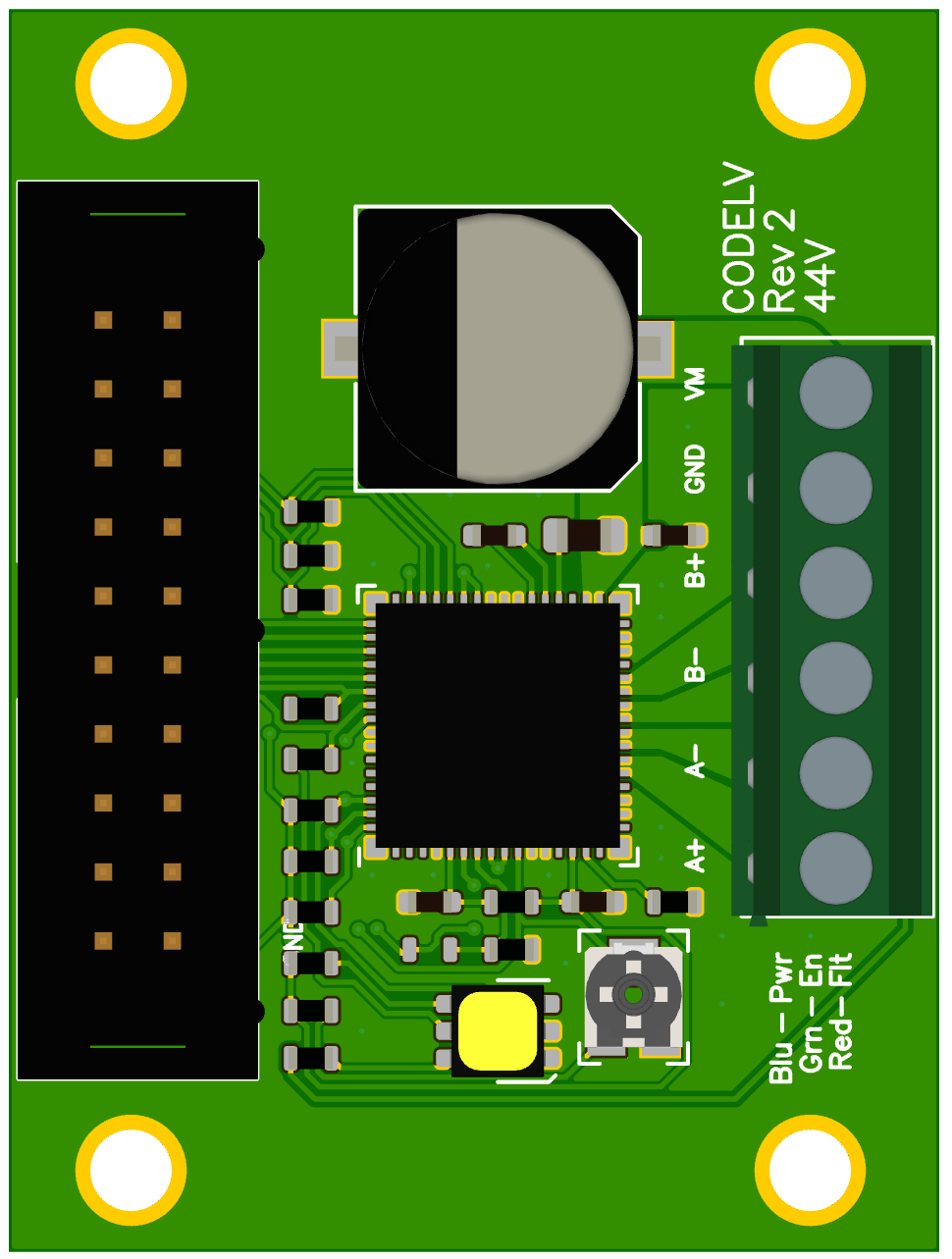
Version 2 features mounting holes, an IDC connector with torque pin inputs, and larger board area to improve heat dissipation.
In order to simplify the design several pins have been hard wired to default values.
The eval board has M3 holes for mounting at 25mm x 40mm (0.984 in x 1.575 in) spacing.
Top of board
Bottom of board
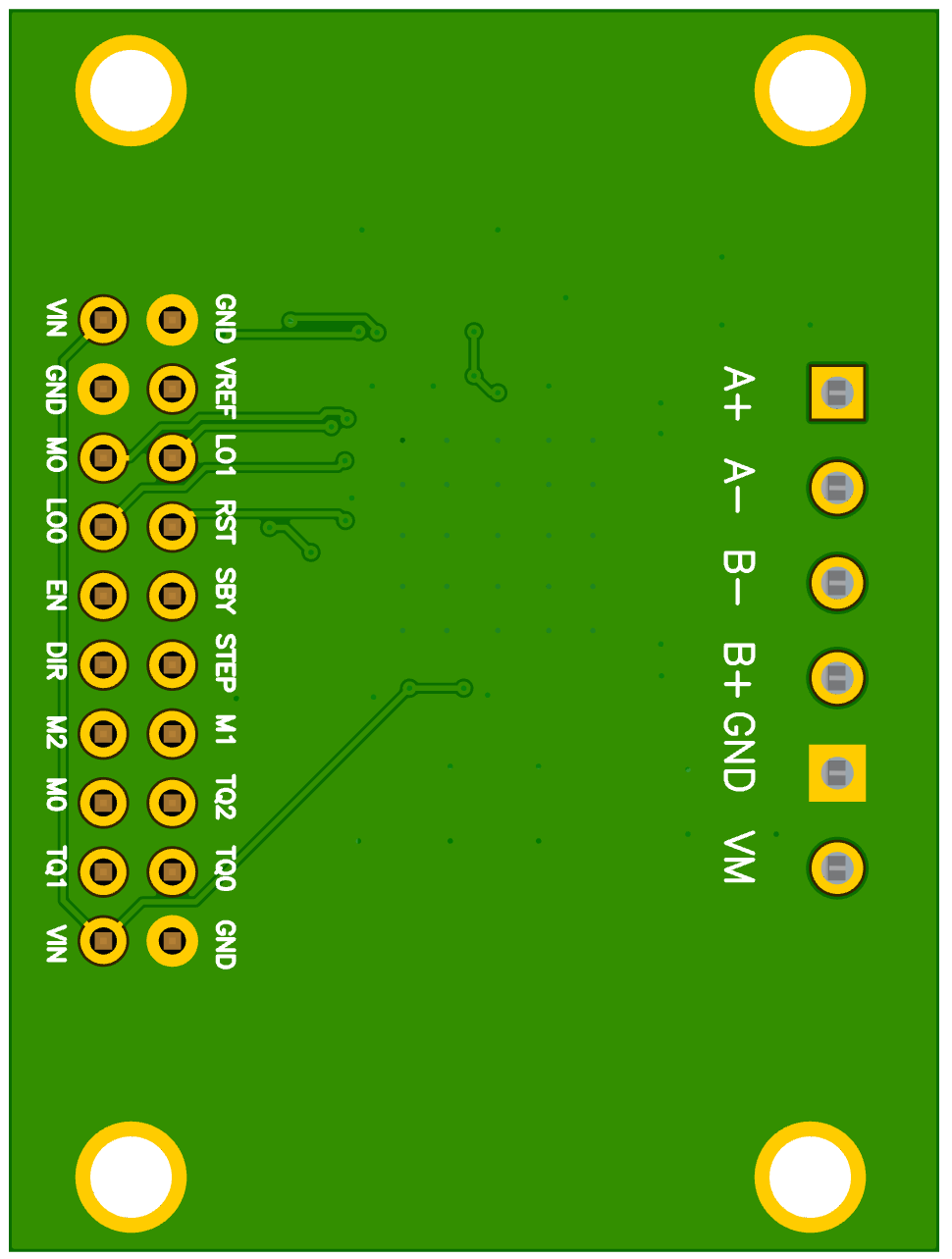
The minimal setup requires:
Warning: VM and VIN do not have reverse polarity protection always double check before plugging it in and turning on power!
Note: Do not set enable high before appling power to VIN
The board has a trimmer to set VREF. The eval board is hard wired to run in resistor less mode with a gain of 1/5 as shown in section 13.2 of the datasheet.
Ilim = 1.56 * Vref
With the motor disconnected, apply VM and measure the voltage between Vref and ground. The adjustment screw is tied to Vref so you can use that to measure the voltage.
Note: I highly recommend putting a meter in-line with one of the coils to get an actual current reading.
The pins M0 to M2 set the micostepping level. I recommend using the highest resolution your software supports as it will reduce vibration and noise.
| M0 | M1 | M2 | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | L | L | Full step resolution |
| L | L | H | Half step resolution |
| L | H | L | Quarter step resolution |
| L | H | H | 1/8 step resolution |
| H | L | L | 1/16 step resolution |
| H | L | H | 1/32 step resolution |
| H | H | L | 1/64 step resolution |
| H | H | H | 1/128 step resolution |
Note: Resolution is not the same as accuracy. The torque available changes based on the step angle which can cause positional errors.
The pins TQ0 to TQ2 set the torque level. These can be used to limit current and heat of the driver. By default torque is set to 100% using 100k pull down resistors.
| TQ0 | TQ1 | TQ2 | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | L | L | Torque 100% |
| L | L | H | Torque 85% |
| L | H | L | Torque 70% |
| L | H | H | Torque 60% |
| H | L | L | Torque 50% |
| H | L | H | Torque 40% |
| H | H | L | Torque 25% |
| H | H | H | Torque 10% |
The eval board features a RGB led to help you check the status of the driver. The LED will be green when the enable pin is high. When power is applied to VM, the LED will turn blue. If VM has power and is enabled both will be on so the LED will look teal.
If there is a fault on the LO0 pin (such as over current or over temp) the red LED will illuminate, making the LED appear white.
You can check the fault by reading the LO0 and LO1 pins. To reset the fault VM must be cycled or the driver must be put into standby.
| LO0 | LO1 | Error |
|---|---|---|
| Hi-Z | Hi - Z | None |
| Hi-Z | L | Motor open load |
| L | Hi-Z | Over current |
| L | L | Thermal shutdown |
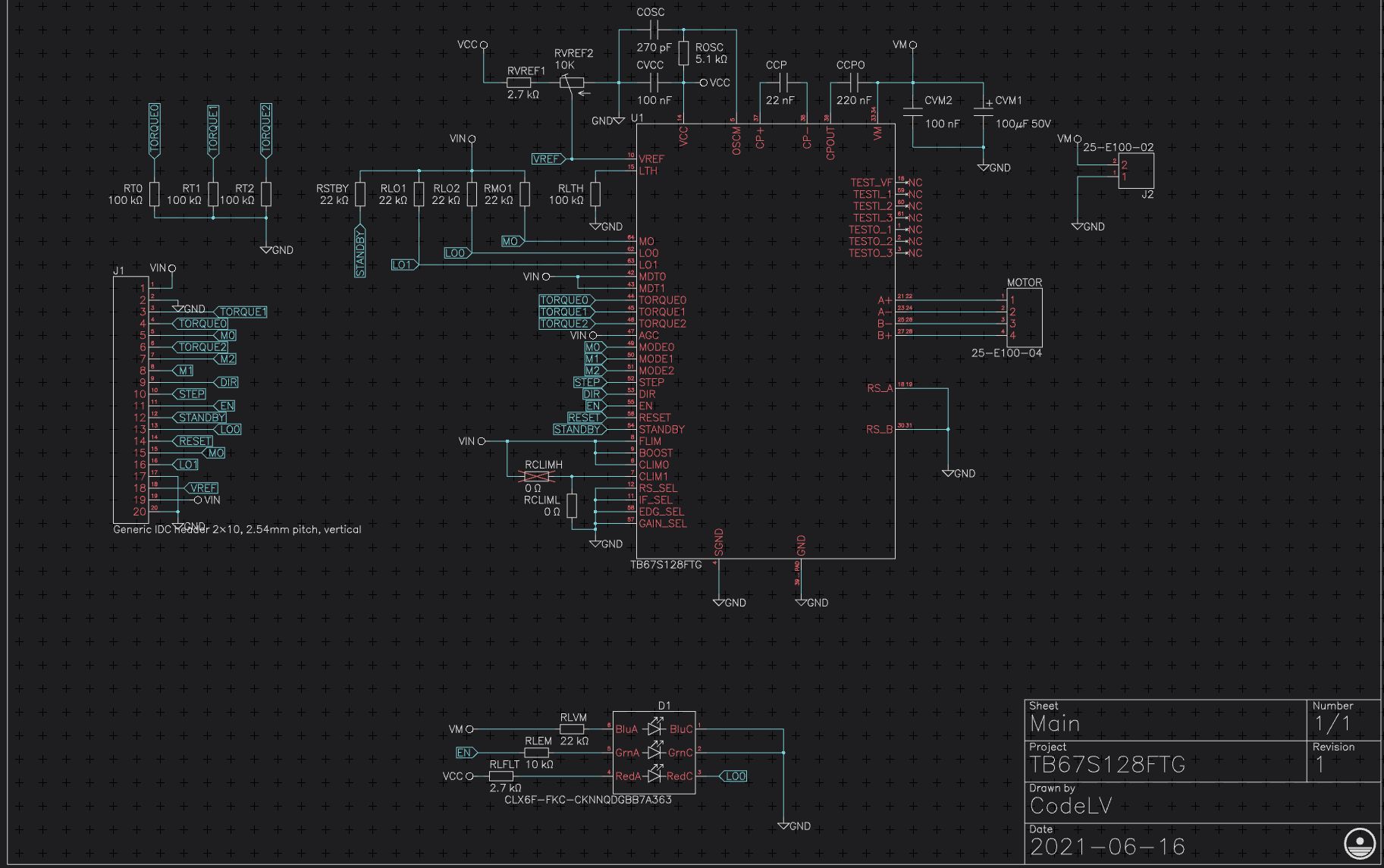
This was designed this using Horizon-EDA. The PCB's were fabbed by JLCPCB. Assembly and reflow is done in house.